FFPE Blocks, Slides, & Sections: Definitions & Use Cases
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples are vital in pathology and biomedical research. This preservation method was established in the late 1800s and has brought incredible understanding to biomedical researchers. Now, FFPE samples provide a long-lasting preserved archive of samples for repeated examinations. Keep reading to learn the stages of a sample collected for FFPE preservation and explore the diverse uses of FFPE tissue samples across different disciplines.

What Are FFPE Tissue Blocks, Slides & Sections?
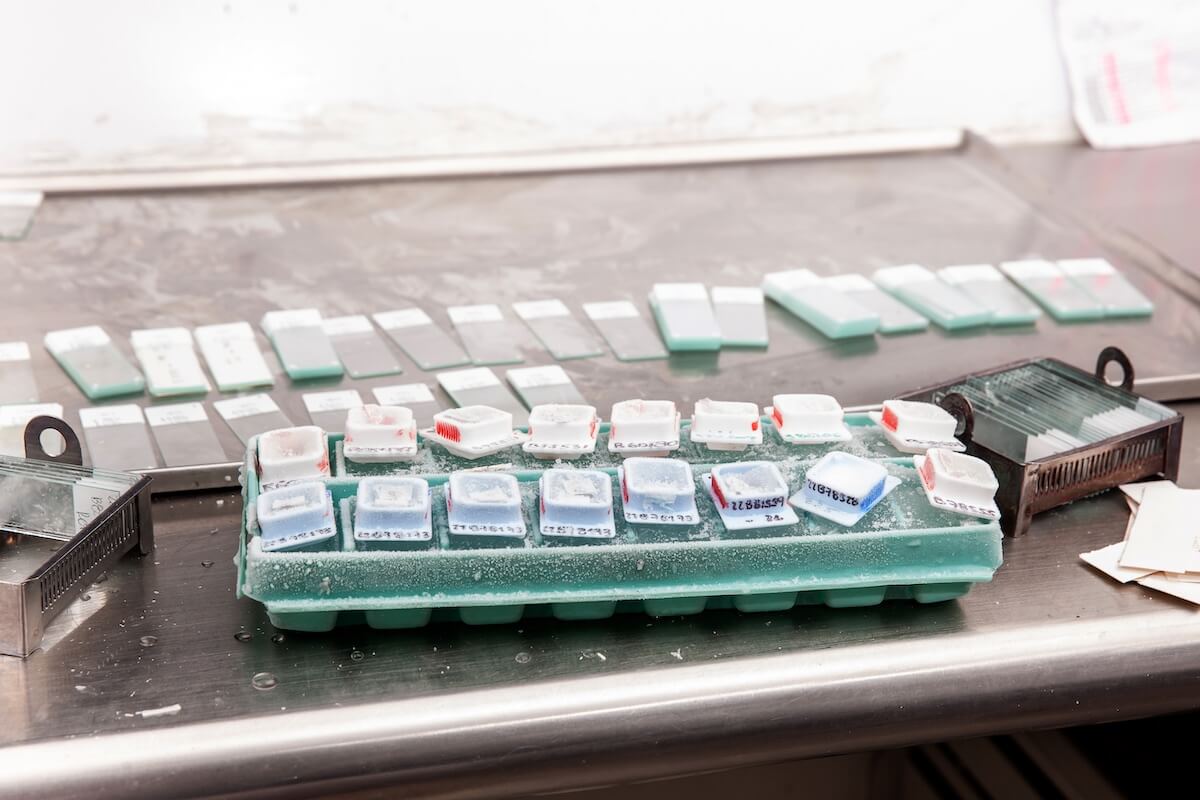
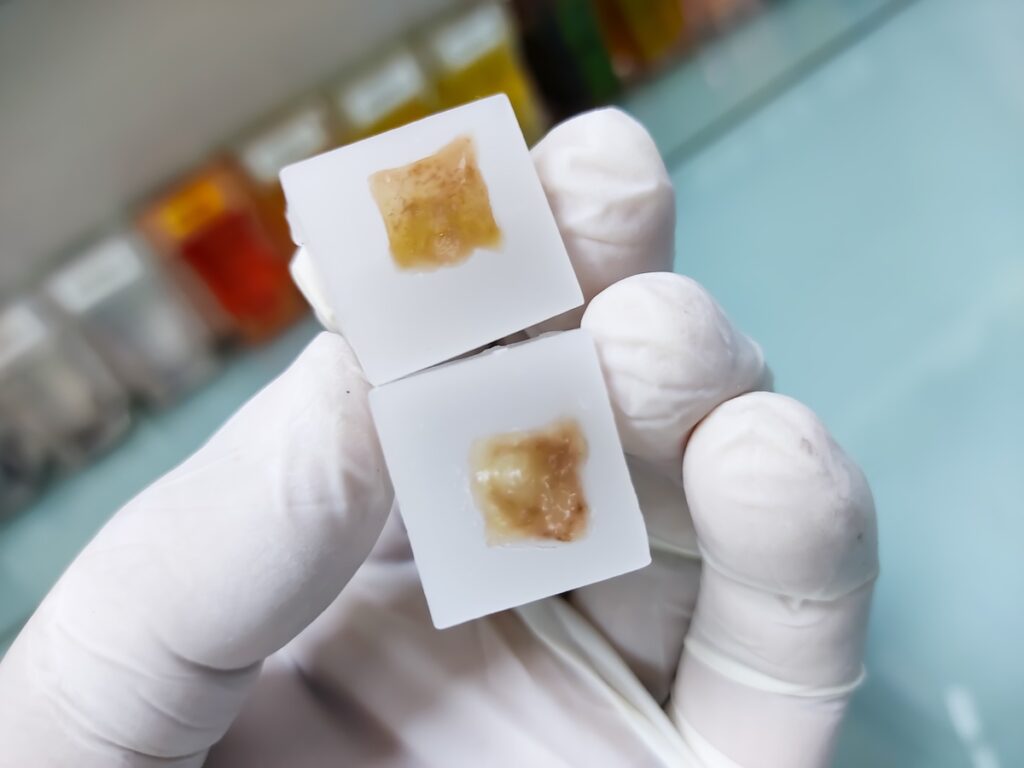
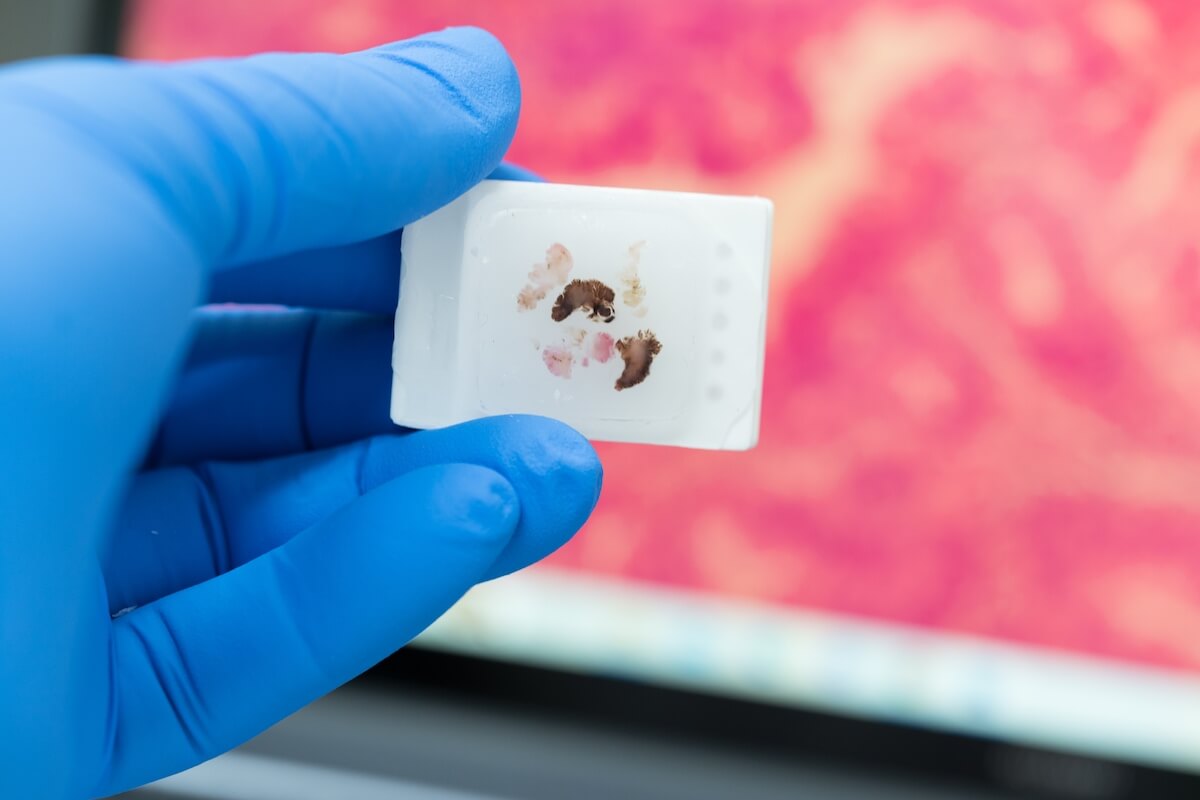
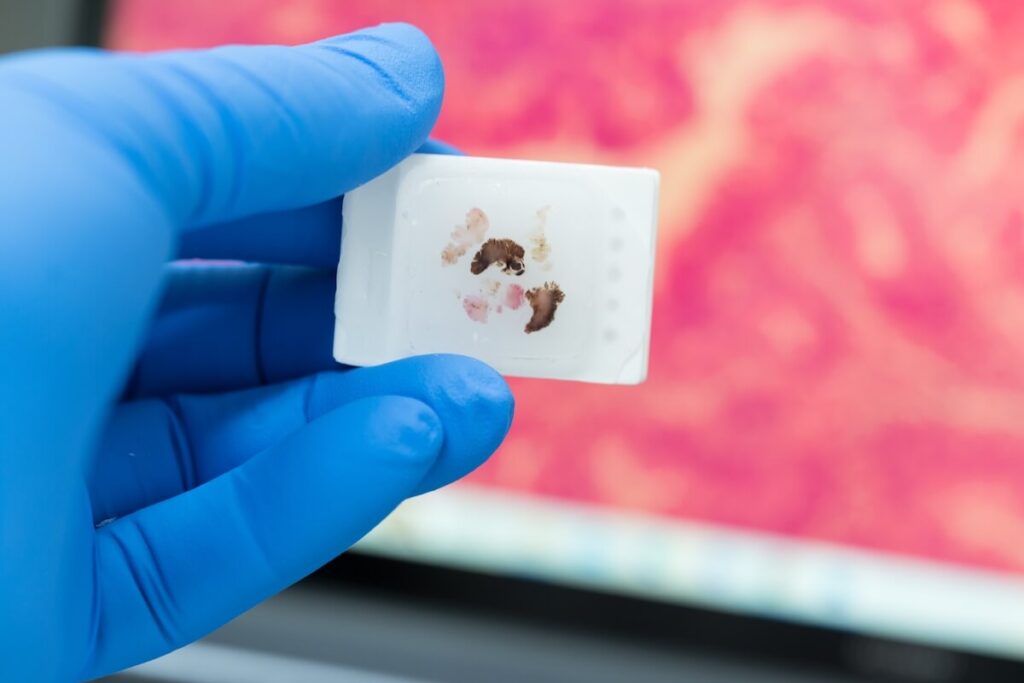
FFPE Tissue Blocks
Collecting tissue to create a formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sample is a process that can take many forms. Doctors have the option to biopsy diseased tissue, healthy tissue, or both. FFPE tissue blocks usually require a biopsy of only a few millimeters of tissue, making the process quick, efficient, and generally painless.
Immediately following the biopsy, the tissue is submerged in formalin for 18–24 hours to preserve the tissue’s pristine condition. Next, the preserved tissue is dehydrated before being embedded in IHC-grade paraffin wax. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is a clinical method that uses antibodies to check for antigens with a fluorescent dye. IHC-grade paraffin wax has the ability to accept these dyes to be used in IHC testing.
By preserving the tissue in this way, researchers can cut sections from the FFPE block for closer examination.
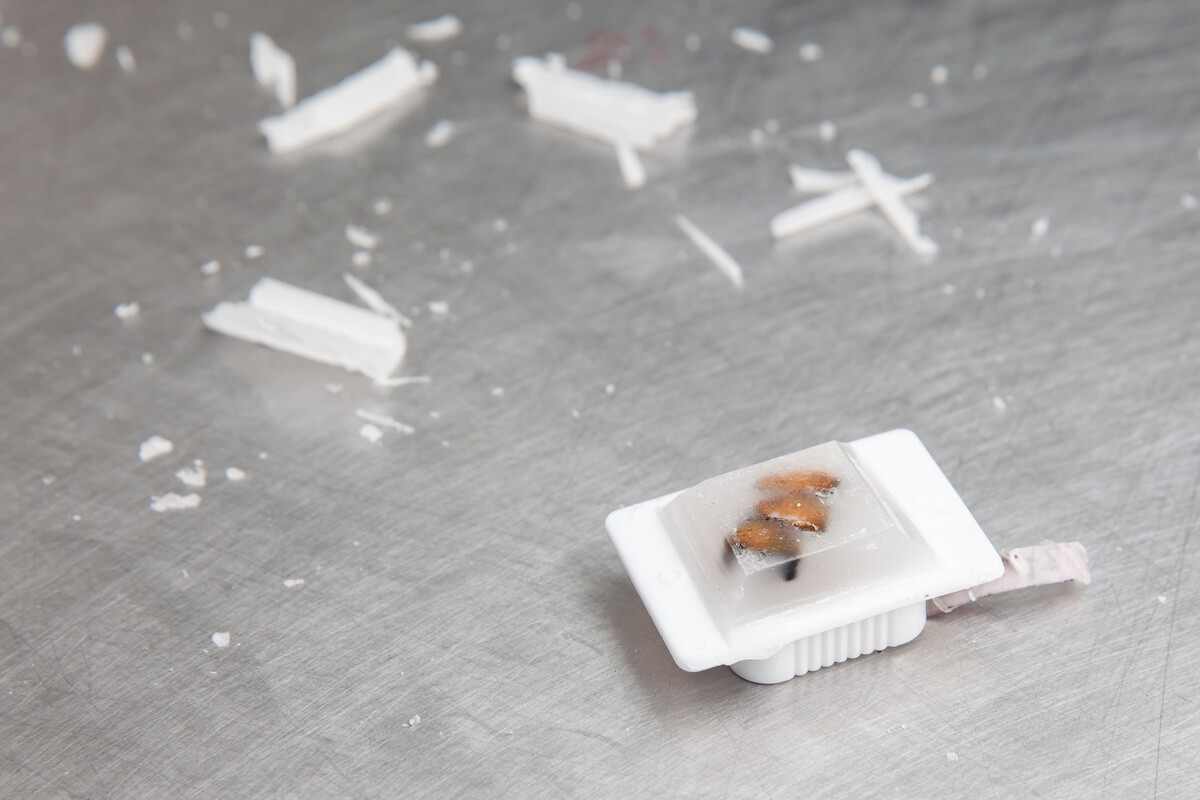
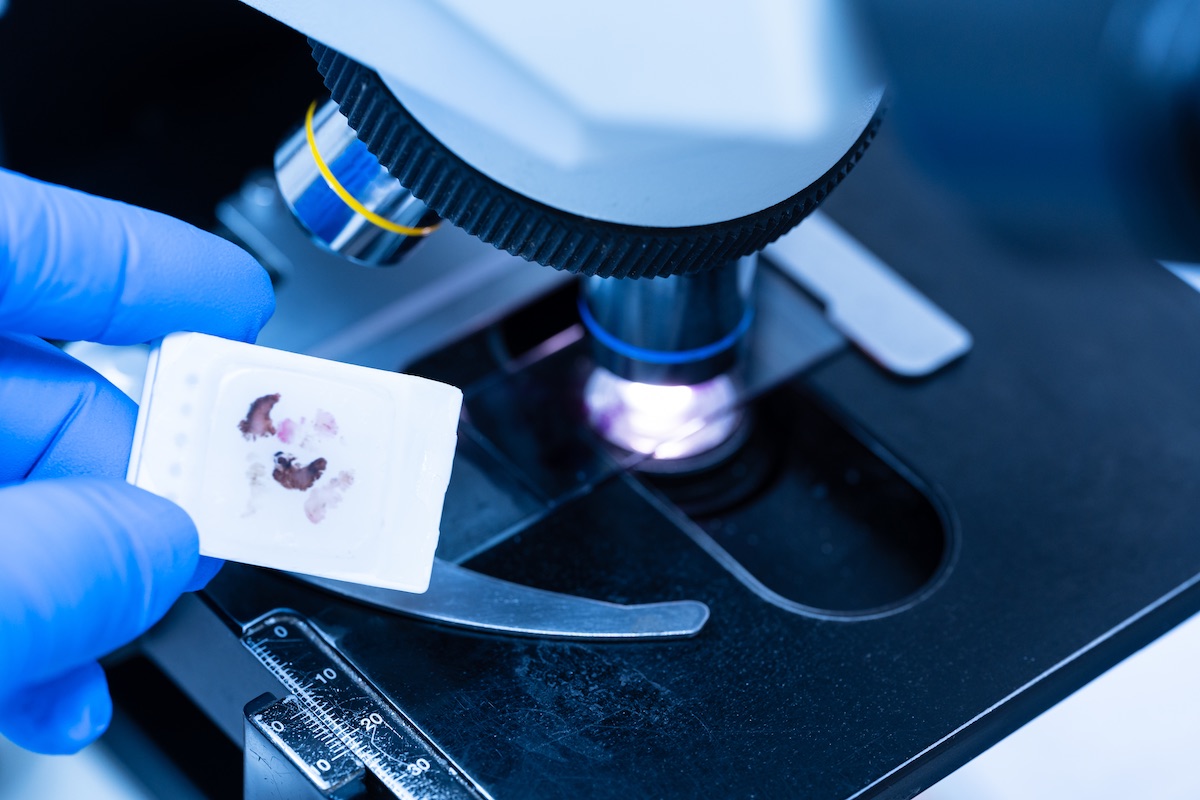
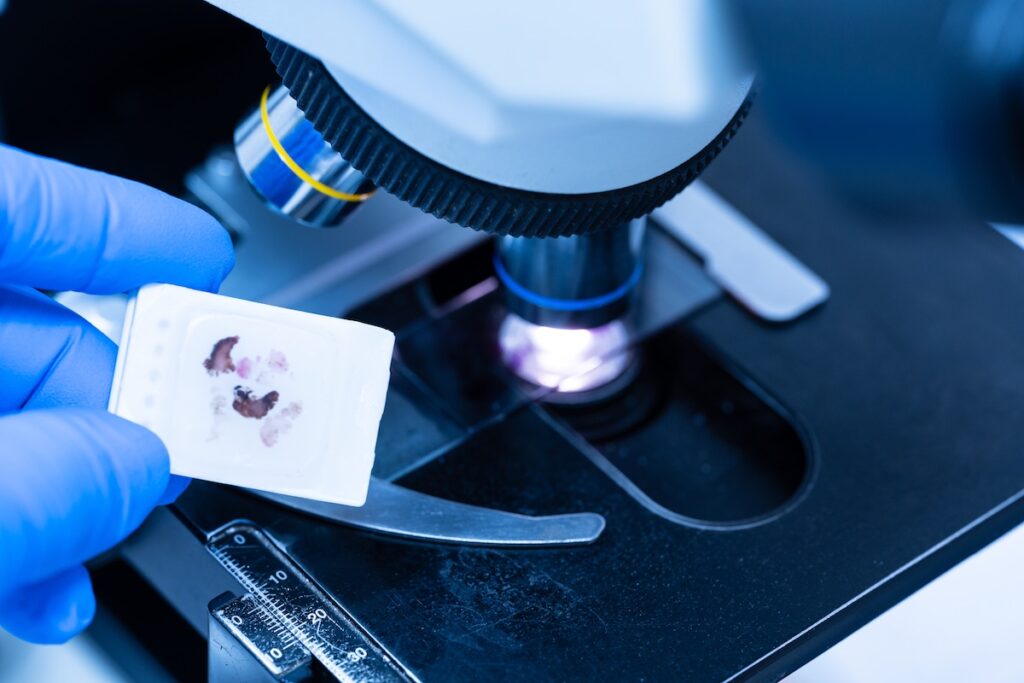
FFPE Tissue Sections
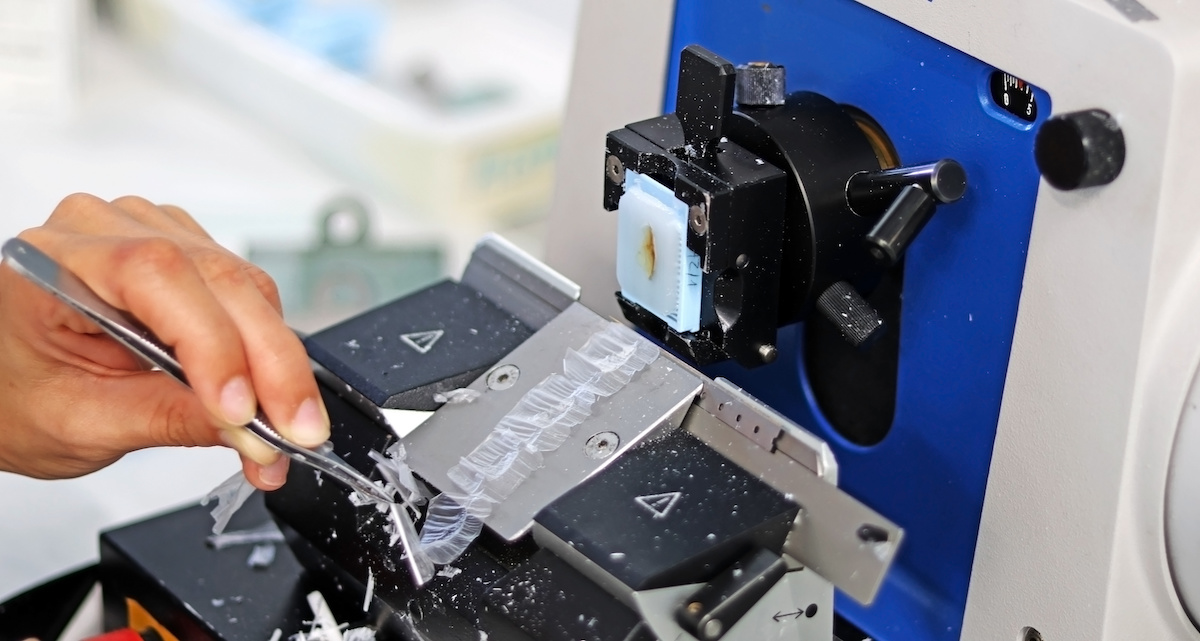
FFPE sections are thin slices of tissue cut from FFPE blocks. These sections are then prepared using a microtome (a device that trims the tissue to precise depths ranging from a few micrometers to several millimeters). FFPE sections are used for a wide range of microscopic studies.
FFPE sections stored in archives have the ability to last up to 20 years! They offer a historical perspective on disease and a clear record of medical advancements. FFPE is a versatile preservation method; sections can be stored at room temperature, making FFPE sections a less expensive option to preserve and study the microscopic structures and the protein makeup of test samples. These sections can be mounted onto slides for examination under a microscope.
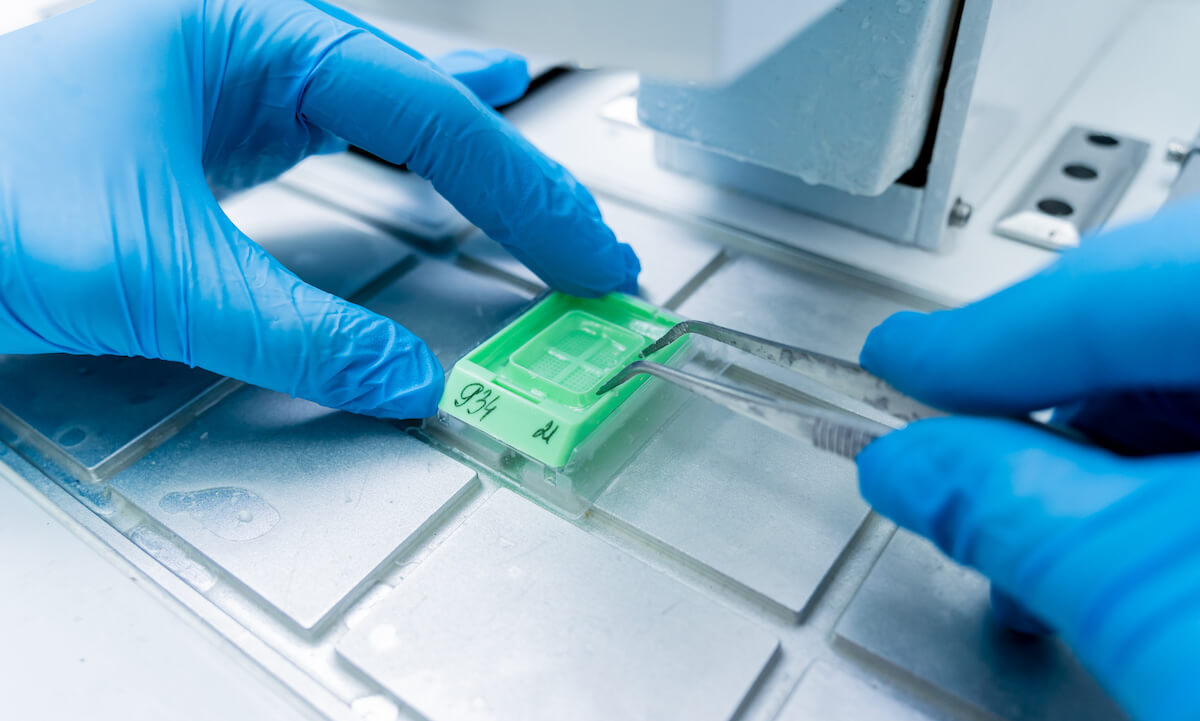
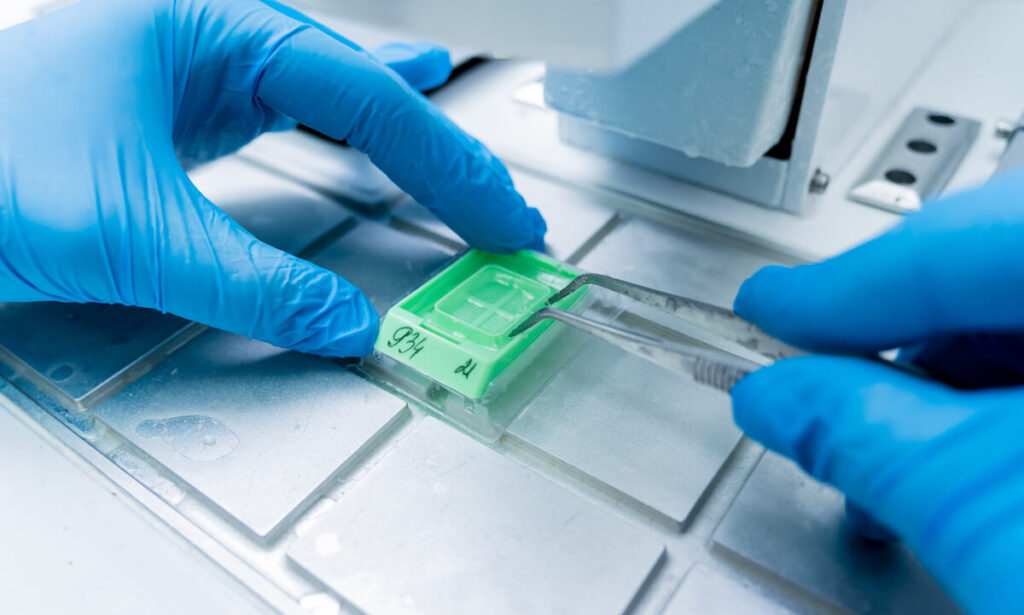
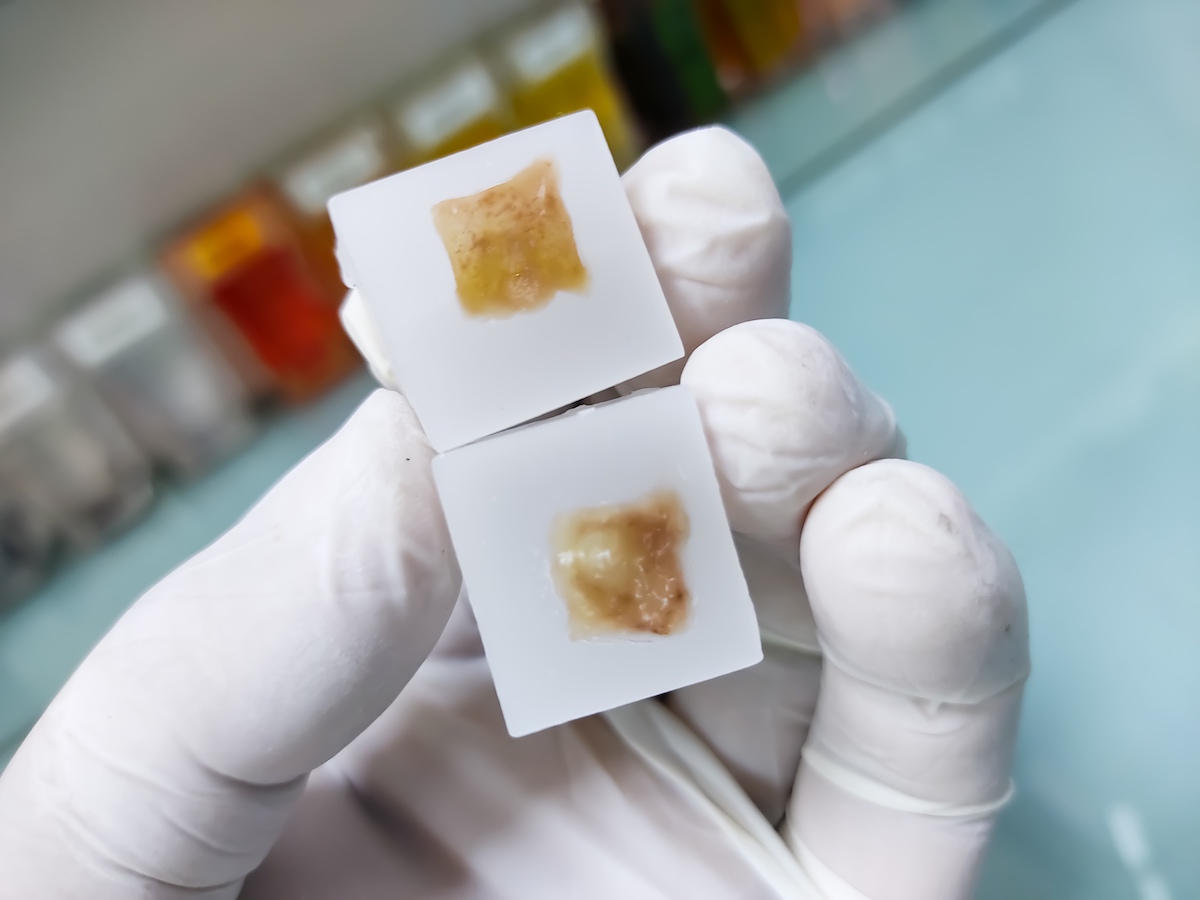
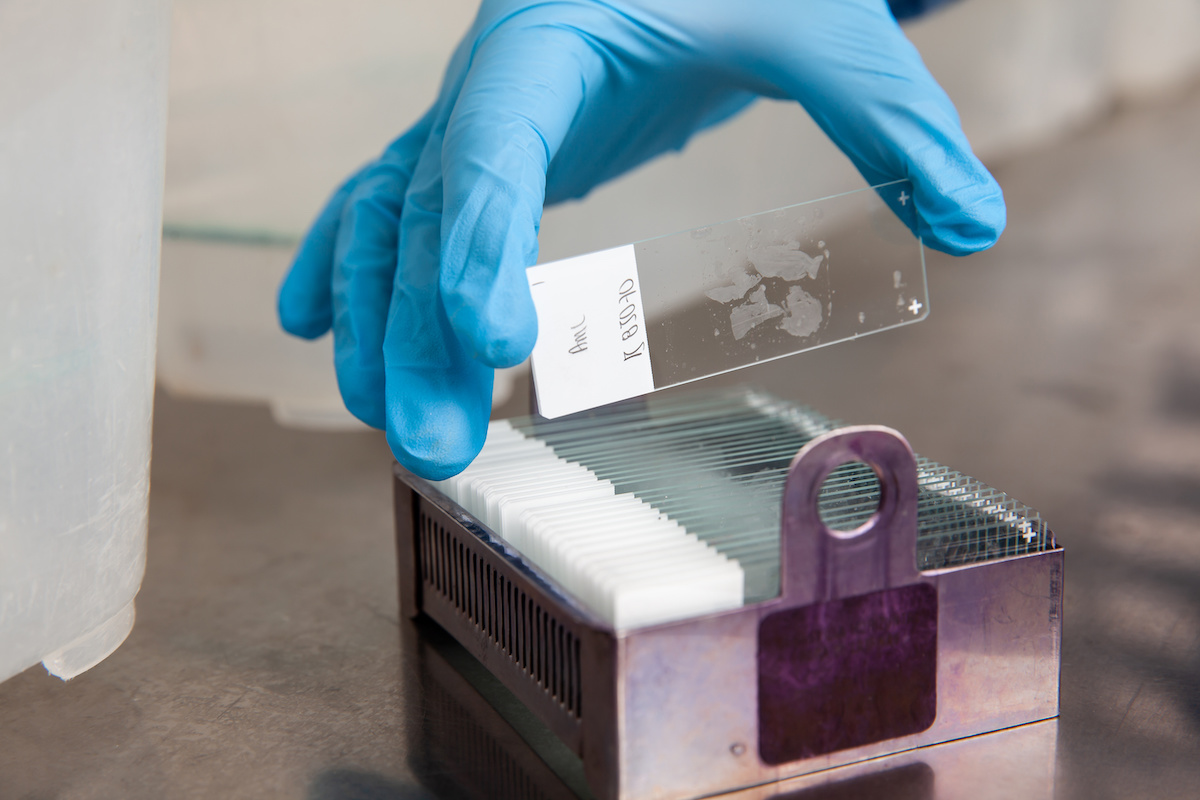
FFPE Tissue Slides
FFPE slides are thin sections of tissue samples mounted onto glass slides from FFPE blocks. These slides are typically stained for microscopic examination using various histological or immunohistochemical techniques. FFPE slides allow pathologists and researchers to visualize tissue morphology and study cellular structure under a microscope.
4 Common Uses of FFPE Tissue Blocks, Slides & Sections
1. Histopathology
Histopathology is the study of the change of tissue over time as a result of a disease. FFPE tissue samples are often used in diagnostic histopathology to diagnose diseases like cancer. Pathologists examine FFPE slides under a microscope to identify irregular cellular structures, tissue architecture, and other pathological features that indicate disease.
2. Molecular Biology Research
Scientists can extract DNA and RNA from FFPE sections to study genetic mutation, gene expression patterns, and epigenetic modifications associated with various diseases.
3. Drug Development
FFPE tissues are frequently used in the drug development process. Researchers use FFPE sections to assess drug efficiency or toxicity.
4. Forensic Pathology
FFPE blocks are valuable in forensic pathology for preserving tissue samples from cases involving biomatter. These samples can be archived for long periods of time, allowing forensic scientists to conduct postmortem examinations and investigations into the cause and manner of death.
FFPE Tissue Samples—A Closer Look at The Future
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tissue samples have become vital in pathology and biomedical research. FFPE blocks, slides, and sections have become a standard in diagnostic histopathology to diagnose diseases since the preservation method’s inception in the 19th century. FFPE tissues are frequently used in the drug development process and forensic pathology to preserve tissue samples from cases involving biomatter. FFPE is a versatile preservation method; FFPE sections can be stored at room temperature, making them less expensive options to preserve and study the microscopic structures and the protein makeup of test samples.
Are you interested in the benefits of FFPE tissue blocks, sections, or slides for your research? Join top-rated academic institutions and biomedical companies that have made Superior BioDiagnostics their choice biobank supplier. Order your FFPE samples today!